Are You Suffering From Failed Back Surgery Syndrome or Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome?
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome, also known as Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome, refers to chronic pain that persists after spine surgery. This condition can result from various issues, including nerve damage or improper healing. Board Certified Dr. Robert J. Nocerini, MD, at Northstar Joint and Spine specializes in diagnosing and treating this challenging condition. Get personalized care and effective solutions for lasting relief. For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 7704 San Jacinto Pl Suite #200 Plano, TX 75024.
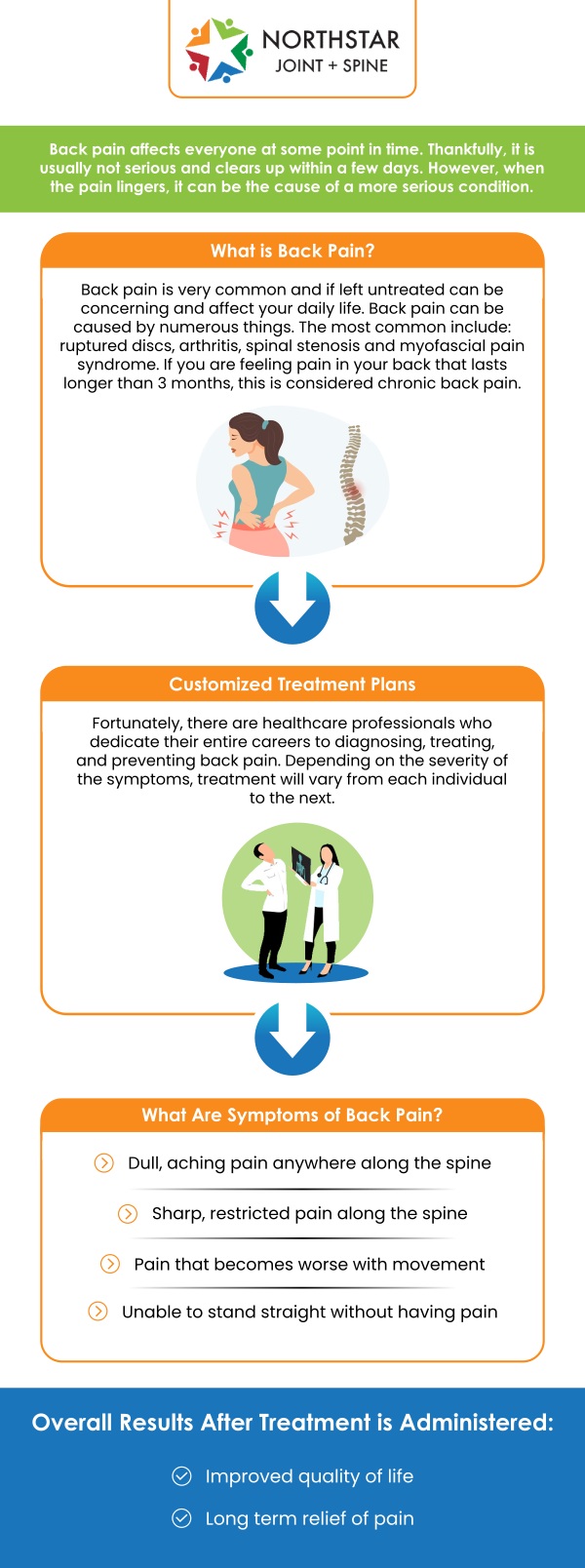
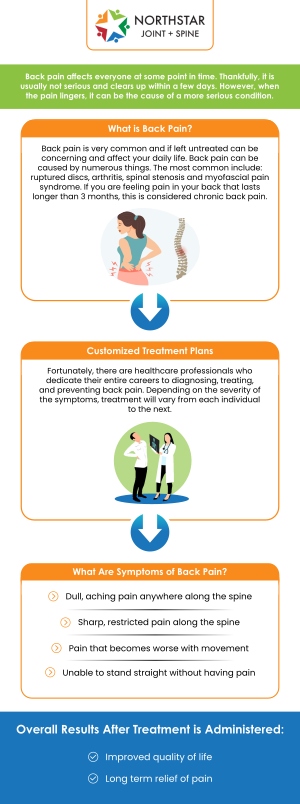
Table of Contents:
What is Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome (PSPS)?
What are the symptoms of persistent spinal pain syndrome?
What are some risk factors for persistent spinal pain syndrome?
What is the treatment for persistent spinal pain syndrome?
Suffering from Failed Back Surgery Syndrome or Persistent Spinal Pain? Dr. Robert J. Nocerini, MD Can Help
Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome (PSPS) is a condition characterized by ongoing back or neck pain that persists even after spine surgery or treatment intended to relieve the discomfort. This syndrome occurs when nerves in the spinal region become compressed or irritated, leading to chronic pain that can extend to the arms or legs. It often follows a failed spinal procedure, such as disc replacement or fusion, though not all cases are surgery-related.
The exact causes of PSPS are varied, and they can include herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or degenerative changes in the spine. In some cases, even after surgery, the pain may not resolve due to the failure of the procedure to fully address the underlying issue, or new problems may develop over time.
Symptoms of PSPS may include constant back or neck pain, radiating pain down the limbs, and in some cases, weakness or numbness. Diagnosing PSPS often involves a thorough medical evaluation, including imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans, to rule out other conditions.
Treatment for PSPS typically focuses on pain management, including physical therapy, medications, or nerve blocks. In more severe cases, further surgery may be necessary to correct the issue. Addressing PSPS often requires a multidisciplinary approach to effectively manage the pain and improve quality of life.
After spine surgery, some patients continue to experience ongoing pain despite the procedure. Common symptoms of Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome (PSPS) include diffuse, dull, and aching pain in the back or legs. Additionally, sharp, pricking, burning, or stabbing pain may be felt in the extremities, contributing to discomfort that lasts long after the surgery.
Failed Cervical Fusion:
This occurs when the bones do not properly fuse or if the body rejects a bone graft used in surgery. Symptoms associated with failed cervical fusion include:
• Persistent neck or back pain
• Stiffness and weakness
• Numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the arms and legs
• Difficulty walking or coordinating hand movements
Post Laminectomy Syndrome (PLS):
PLS affects a small number of patients who undergo a laminectomy. Symptoms of PLS can resemble the pain felt before surgery, including:
• Persistent dull or achy pain
• Sharp, prickling, or stabbing sensations
Pseudoarthrosis (Failed Fusion Syndrome):
This condition occurs when a spinal fusion fails to heal properly. Symptoms may include:
• Ongoing back pain
• Limited mobility and stiffness
• Muscle spasms and insomnia due to discomfort
• Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the extremities
In all cases, addressing PSPS may require further medical intervention, such as pain management, physical therapy, or additional surgery.
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome (PSPS) after spinal surgery. Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors, as it impairs healing and increases the chance of complications. The formation of scar tissue around the surgical site can also contribute to ongoing pain, leading to limited mobility and discomfort.
Other contributing factors include persistent or recurring disc disease at adjacent levels of the spine, which may worsen over time. Continued pressure from conditions like spinal stenosis can exacerbate symptoms, as it places additional strain on the nerves. Spinal instability, where the vertebrae shift or fail to stabilize properly, can also lead to long-term pain.
Pseudoarthrosis, or failed fusion, occurs when the spine fails to heal correctly after fusion surgery, leading to continued discomfort. Additionally, nerve damage within the affected area can cause chronic pain, numbness, and weakness. These risk factors can complicate recovery and contribute to the persistence of pain after spine surgery.
Managing Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome (PSPS) typically involves a combination of therapies aimed at alleviating pain and improving function. Physical therapy is commonly recommended to help strengthen muscles, improve flexibility, and reduce discomfort. Nerve blocks and medication, including injections, can also provide targeted relief to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. For some patients, a chronic pain management program may be necessary for long-term care.
When no clear cause for the back pain is found, more advanced treatments like spinal cord stimulation (SCS) or the use of narcotic pumps can help control pain. Non-medical approaches, such as walking within tolerance, applying cold packs for inflammation, and adjusting posture for sleep and sitting, are often recommended. If symptoms worsen or fail to improve, revision surgery may be necessary to address the ongoing issues.
At Northstar Joint and Spine, Board-Certified Dr. Robert J. Nocerini, MD, helps patients manage the challenges of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS) and Persistent Spinal Pain Syndrome with precision and compassion. These conditions can cause ongoing discomfort even after surgical intervention, making daily life difficult. Dr. Nocerini focuses on identifying the true source of post-surgical pain and creating individualized strategies that aim to improve function, stability, and comfort.
Why Choose Dr. Robert J. Nocerini:
• Board-Certified specialist in pain management
• Expertise in evaluating complex post-surgical spine conditions
• Comprehensive, patient-focused approach to diagnosis and care
• Dedicated to restoring comfort, mobility, and confidence
• Emphasis on long-term pain relief and improved quality of life
For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 7704 San Jacinto Pl Suite #200 Plano, TX 75024. We serve patients from Plano TX, Willow Bend TX, Frisco TX, Allen TX, Addison TX, North Dallas TX, and surrounding areas.

Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Need
▸ Back Pain
▸ Shoulder Pain
▸ Chronic Pain
▸ Epidural Steroid Injections
▸ Spinal Cord Stimulation
▸ Viscosupplementation
▸ Genicular Nerve Blocks
▸ Facet Injections
▸ Joint Injections
▸ Sacroiliac Joint Injections
▸ Lumbar and Cervical
▸ Facet Medial Branch Blocks
▸ Diagnostic Nerve Blocks
▸ Medication Management
▸ Neck Pain Doctor
▸ Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
▸ Headaches
▸ Suboxone
▸ Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
▸ Spine
▸ Joints
▸ Muscles
▸ Bones

Additional Services You May Need
▸ Back Pain
▸ Shoulder Pain
▸ Chronic Pain
▸ Epidural Steroid Injections
▸ Spinal Cord Stimulation
▸ Viscosupplementation
▸ Genicular Nerve Blocks
▸ Facet Injections
▸ Joint Injections
▸ Sacroiliac Joint Injections
▸ Lumbar and Cervical
▸ Facet Medial Branch Blocks
▸ Diagnostic Nerve Blocks
▸ Medication Management
▸ Neck Pain Doctor
▸ Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
▸ Headaches
▸ Suboxone
▸ Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
▸ Spine
▸ Joints
▸ Muscles
▸ Bones