Neuropathy Treatment for Legs and Feet in Plano, TX
If you experience symptoms like numbness, tingling, or burning pain in your legs and feet, it may be due to neuropathy. We offer treatment for neuropathy in the legs and feet in Plano, led by board-certified Dr. Robert Nocerini, MD. Receive personalized care designed to improve nerve function and reduce discomfort effectively. Contact us today for more information or schedule an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 7704 San Jacinto Pl Suite #200 Plano, TX 75024.
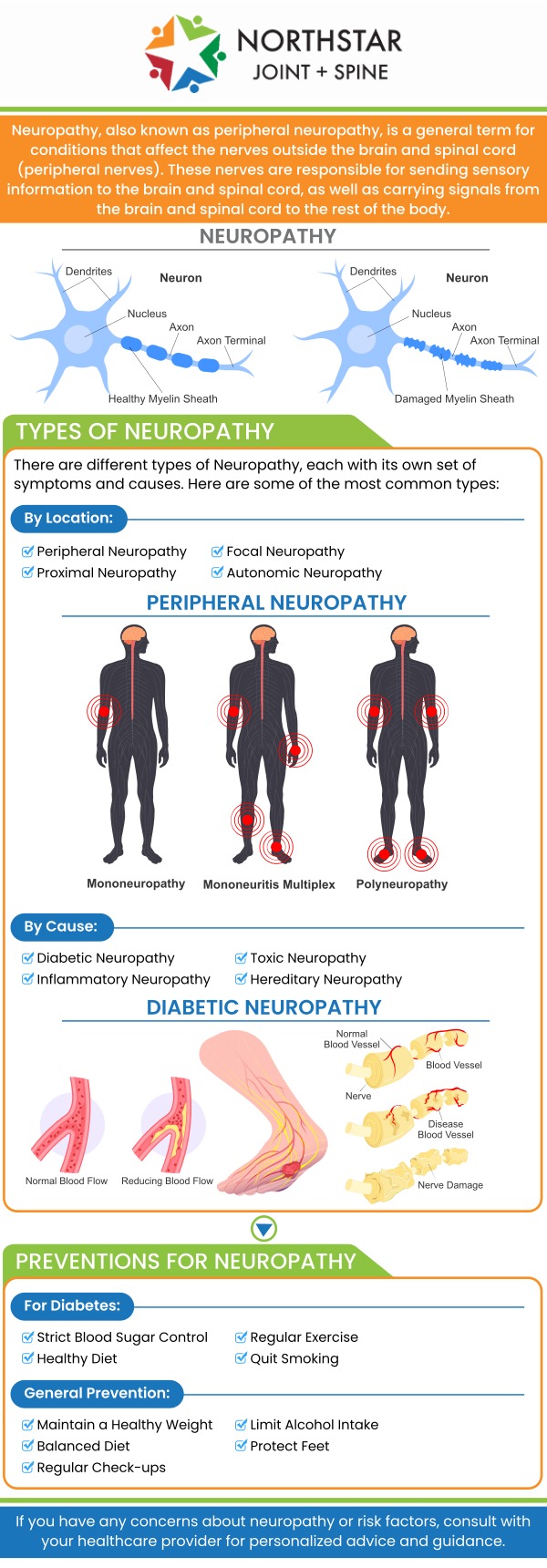
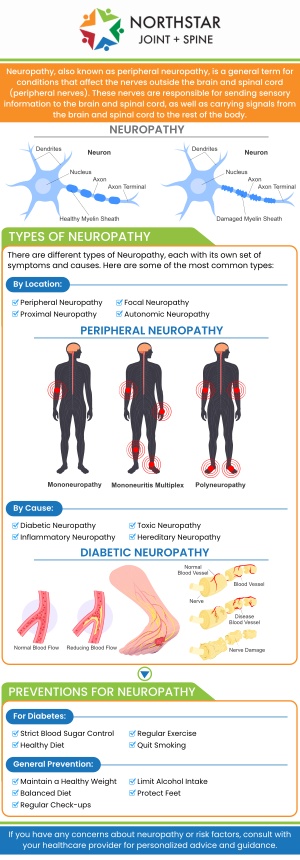
Table of Contents:
What causes neuropathy in the feet and legs?
What does neuropathy feel like in the legs?
Can neuropathy in the legs and feet be reversed or cured?
When should I see a doctor for neuropathy in my legs and feet?
How Dr. Robert J. Nocerini, MD, at Northstar Joint and Spine Provides Relief for Neuropathy in the Legs and Feet
Neuropathy in the feet and legs, also known as peripheral neuropathy, occurs when the peripheral nerves are damaged or malfunction. The most common cause is diabetes, where elevated blood sugar levels gradually harm nerve fibers, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and burning sensations. Other causes include vitamin deficiencies, especially B vitamins, autoimmune diseases, infections, exposure to toxins, and certain medications. Physical nerve compression, such as from repetitive movements or pressure on nerves, can also damage nerves and contribute to neuropathy.
In addition to these factors, chronic conditions like kidney disease and alcoholism may increase the risk of developing neuropathy. Some cases are hereditary or idiopathic, meaning the cause is unknown. Symptoms usually develop gradually and worsen over time, affecting sensation and muscle control in the feet and legs. Early detection and addressing the underlying cause are essential for managing symptoms effectively and preventing further nerve damage. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and improving quality of life.
Neuropathy in the legs often causes a range of unusual sensations that can vary from person to person. Many individuals experience numbness or a loss of sensation, making it difficult to detect temperature changes or pain. Tingling or “pins and needles” sensations typically begin in the toes and can slowly progress upward. Some people describe burning or sharp, stabbing pains that are often worse at night. These symptoms can make standing, walking, or even wearing shoes uncomfortable.
In addition to sensory changes, neuropathy may cause muscle weakness, cramps, or a feeling of heaviness in the legs. This can lead to balance issues and increase the risk of falls. Some patients also experience heightened sensitivity, where even light touch becomes painful. The severity and frequency of symptoms can fluctuate, significantly impacting daily activities and overall quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing these symptoms and preventing further nerve damage.
Neuropathy in the legs and feet can sometimes be managed effectively, but whether it can be reversed or cured depends largely on its underlying cause. In cases where neuropathy is caused by factors like vitamin deficiencies, infections, or exposure to toxins, treating the root cause early may lead to significant improvement or even reversal of symptoms. For example, correcting vitamin deficiencies or controlling blood sugar in diabetic patients can help prevent further nerve damage and improve nerve function.
However, if neuropathy results from chronic conditions like long-standing diabetes or hereditary disorders, complete reversal is often challenging. In these cases, treatment focuses on managing symptoms, slowing progression, and improving quality of life. Advances in medical therapies, such as medications, physical therapy, and interventional treatments, can provide significant relief. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial to maximize the potential for recovery and minimize permanent nerve damage.
You should see a doctor for neuropathy in your legs and feet as soon as you notice persistent or worsening symptoms. Early signs include numbness, tingling, burning sensations, or sharp pains that affect your ability to walk or perform daily activities. If these symptoms interfere with your balance, coordination, or cause muscle weakness, it’s important to seek medical evaluation promptly. Early diagnosis allows for timely treatment, which can prevent further nerve damage and improve outcomes.
Additionally, if you have risk factors such as diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or a family history of neuropathy, regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential. Sudden onset of symptoms, severe pain, or loss of bladder or bowel control also warrant immediate medical attention. Consulting a specialist early can help identify the underlying cause, initiate appropriate treatments, and develop a personalized management plan to reduce symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Board-certified Dr. Robert J. Nocerini, MD, at Northstar Joint and Spine specializes in providing targeted relief for neuropathy in the legs and feet. With his extensive experience in treating nerve-related pain, Dr. Nocerini understands how neuropathy can significantly impact daily life, including mobility and comfort. At Northstar Joint and Spine, he utilizes a comprehensive and personalized approach to ensure that every patient receives the most effective treatment tailored to their specific needs. Key treatment options include:
Thorough Diagnosis: Dr. Nocerini starts by conducting a detailed evaluation to pinpoint the exact cause of the neuropathy, allowing him to develop an individualized treatment plan.
Non-Invasive Therapies: For many patients, he recommends physical therapy, nerve stimulation, and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate pain and improve function.
Advanced Interventional Procedures: For more severe symptoms, Dr. Nocerini may suggest treatments like injections or minimally invasive procedures to reduce pain and promote healing.
Ongoing Patient Support: Dr. Nocerini emphasizes ongoing care, ensuring that patients are well-informed and supported throughout their treatment journey.
With his expertise and compassionate approach, Dr. Nocerini helps patients manage and alleviate neuropathy in the legs and feet, aiming to restore comfort and mobility for a better quality of life. Contact us today for more information or schedule an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 7704 San Jacinto Pl Suite #200 Plano, TX 75024. We serve patients from Plano TX, Willow Bend TX, Frisco TX, Allen TX, Addison TX, North Dallas TX, and surrounding areas.

Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Need
▸ Back Pain
▸ Shoulder Pain
▸ Chronic Pain
▸ Epidural Steroid Injections
▸ Spinal Cord Stimulation
▸ Viscosupplementation
▸ Genicular Nerve Blocks
▸ Facet Injections
▸ Joint Injections
▸ Sacroiliac Joint Injections
▸ Lumbar and Cervical
▸ Facet Medial Branch Blocks
▸ Diagnostic Nerve Blocks
▸ Medication Management
▸ Neck Pain Doctor
▸ Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
▸ Headaches
▸ Suboxone
▸ Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
▸ Spine
▸ Joints
▸ Muscles
▸ Bones

Additional Services You May Need
▸ Back Pain
▸ Shoulder Pain
▸ Chronic Pain
▸ Epidural Steroid Injections
▸ Spinal Cord Stimulation
▸ Viscosupplementation
▸ Genicular Nerve Blocks
▸ Facet Injections
▸ Joint Injections
▸ Sacroiliac Joint Injections
▸ Lumbar and Cervical
▸ Facet Medial Branch Blocks
▸ Diagnostic Nerve Blocks
▸ Medication Management
▸ Neck Pain Doctor
▸ Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
▸ Headaches
▸ Suboxone
▸ Peripheral Nerve Stimulation
▸ Spine
▸ Joints
▸ Muscles
▸ Bones